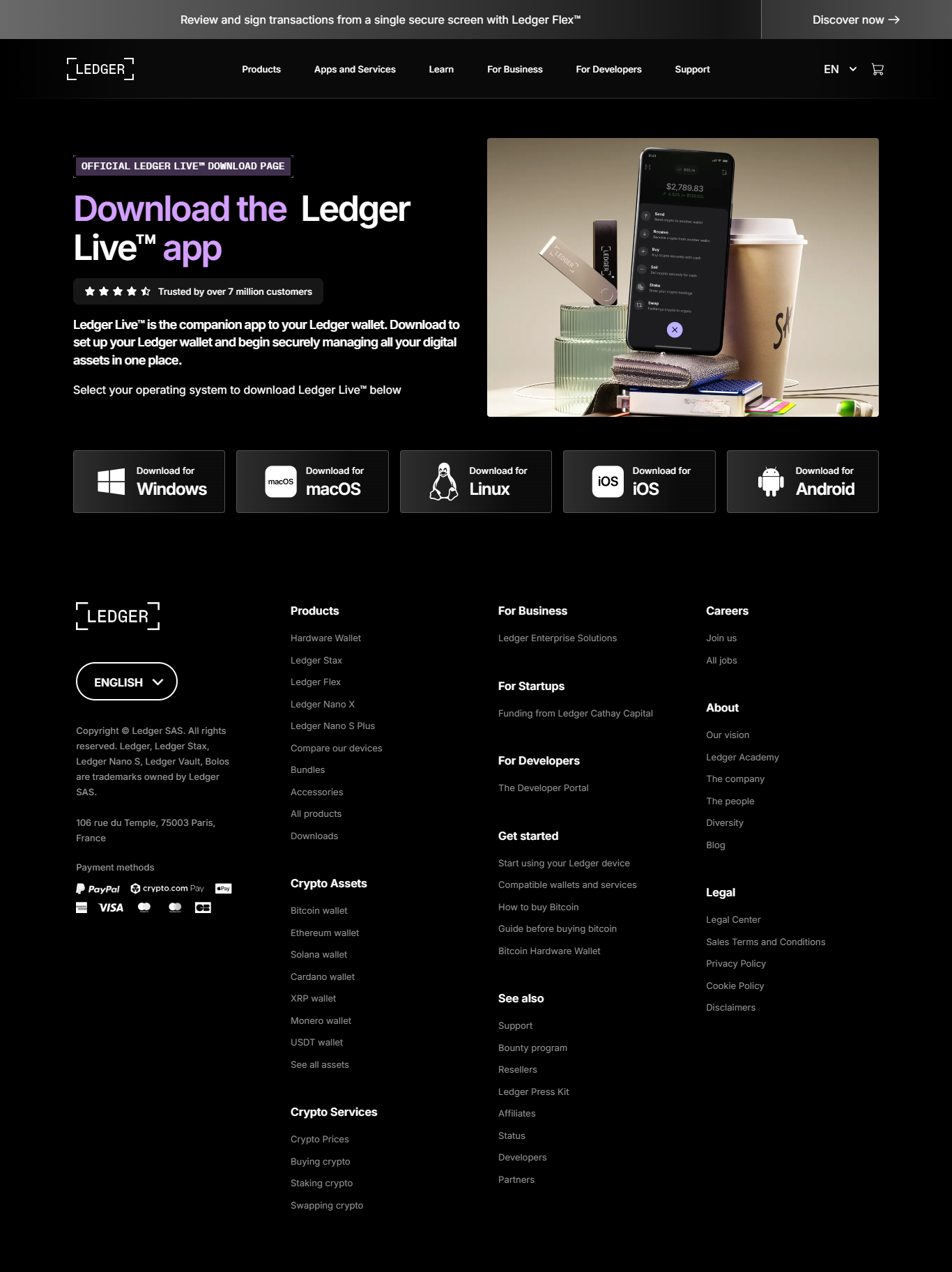
What this guide covers
This guide explains the safe, high-level steps for getting started with a hardware wallet and its companion software. Topics include downloading the official Ledger Live application, initializing a Ledger device, verifying authenticity, installing asset-specific apps, and applying best security practices.
Why use a hardware wallet?
Hardware wallets provide a secure environment for private keys by keeping them offline inside a dedicated secure element. This physical isolation reduces the risk of theft from malware, phishing, or compromised computers and phones. For anyone storing meaningful cryptocurrency, a hardware wallet is an effective tool for self-custody.
Step 1 — Download Ledger Live (official source)
Always obtain the companion software from the vendor’s verified download page. The official download page will use HTTPS and present a legitimate domain. Do not download Ledger Live or any wallet manager from unverified third-party links, social posts, or emails. After downloading, install the app for your platform (Windows, macOS, Linux) or install the official mobile app from the Apple App Store or Google Play Store.
Step 2 — Unbox and inspect your hardware device
When you receive a hardware wallet, inspect the packaging and the device for tamper-evidence. The unit should arrive sealed and include an instruction leaflet and recovery phrase cards. If anything looks suspicious — damaged seals, missing documentation, or unknown sellers — pause and contact the official vendor before proceeding.
Step 3 — Initialize the device
Power on the device and follow the on-screen prompts. Typical initialization steps:
- Choose to set up as a new device or restore from an existing recovery phrase.
- Create a PIN code — this protects the device if it is lost or stolen.
- Write down the displayed recovery phrase (usually 24 words) on the supplied backup sheet. Store this offline and secure.
Critical: Never enter your recovery phrase into a computer, phone, or website. The recovery phrase is the only way to restore access to your funds.
Step 4 — Verify device authenticity
Most reputable vendors provide a means to verify the device’s firmware and authenticity through their official software. After connecting the device to the desktop or mobile app, allow the app to perform its authenticity checks. If the app reports any issues or warnings, stop and consult official support channels.
Step 5 — Install coin/asset apps
Different blockchains typically require a small, dedicated app installed on the device (for example, Bitcoin or Ethereum). Open the companion software’s device or app manager and install only the apps you need. Apps can be removed and reinstalled without losing access to funds, since addresses are derived from your recovery phrase.
Adding accounts
After installing the necessary assets’ apps, add accounts inside the companion software to monitor balances and transactions. The software queries the blockchain for addresses associated with your device and displays balances without exposing private keys.
Step 6 — Send and receive safely
When sending funds, always confirm the recipient address and amount on the device screen before approving. This step prevents malware on your computer from altering transaction details. For receiving funds, verify the receive address shown in the app with the address displayed on your device.
Staking, swaps, and extras
Many companion apps now allow you to stake supported tokens, swap assets via integrated partners, and view NFTs. These actions still require on-device confirmation for any transaction that moves or delegates funds. Read platform-specific documentation to understand fees and lockup rules before staking.
Firmware and software updates
Keep device firmware and companion software up to date. Updates often include security improvements and new features. Always apply updates through the official application and never use unknown or third-party firmware. Before major firmware updates, ensure you have secure access to your recovery phrase in case device reinitialization is required.
Security best practices
- Store your recovery phrase offline in at least one secure location; consider multiple geographic backups.
- Never share your recovery phrase or private keys — no legitimate support team will ever request them.
- Use a strong device PIN and enable any available passphrase or advanced security options if you understand their implications.
- Beware of phishing attempts: verify domain names, and do not click links in unsolicited emails.
- Prefer hardware-backed backups (steel plates, secure safes) to paper where appropriate for long-term storage.
Troubleshooting common issues
Common problems and simple checks:
- Device not recognized: try a different cable or USB port, ensure the device screen is unlocked and the correct app is open.
- App install fails: check available device storage and remove unused apps if necessary.
- Firmware update interrupted: reconnect the device and retry using the official app; if unsure, consult official support resources.
If problems persist, always consult vendor support or verified community resources rather than sharing sensitive recovery details publicly.
Understanding recovery and restoration
If your device is lost, stolen, or damaged, you can restore access to your funds using the recovery phrase on a new compatible device. Practice caution: restoration is a sensitive operation — perform it only on trusted hardware in a secure environment.
Privacy and operational security
Using a hardware wallet enhances security but does not automatically provide anonymity. Consider privacy tools and good operational security (OPSEC) if you wish to reduce address linkage and on-chain traceability. Use new addresses for different purposes when appropriate and be mindful of metadata leakage through exchanges or third-party services.
Further learning
To expand your knowledge, read vendor documentation, community guides, and reputable security blogs. Practical exercises—like setting up a test wallet with small amounts—are useful to gain confidence before moving substantial funds.
Final notes
Hardware wallets, when used correctly, are one of the most reliable ways to keep cryptocurrency keys secure. The combination of an offline secure element, a strong recovery backup, and cautious daily habits significantly reduces many common risks faced by crypto users.
This is an educational demo — do not enter private data here